Stopping the spread of misinformation starts with you. A quick peek at the comment section of a random AI-generated video will show that not everyone is equipped with the tools to detect it. Social pages may use this type of content to boost clicks, views, and interactions, all while ensuring viewers what they’re seeing is authentic.
An audience that is desensitized to AI may be more likely to share more harmful information or imagery without question. Developing a toolbox to detect AI in less consequential imagery can help users protect themselves and stay vigilant.
Where is the content being posted?
This footage can be seen across social platforms. A cursory search for cute animals on Facebook provides examples of fuzzy ‘penguins', pocket-sized ‘critters’, and ‘animals’ posing with ‘babies.’ That same search on Instagram spits out photos of pink ‘polar bears’, petite ‘ponies’, and a ‘capybara’ wearing swim goggles. TikTok is much of the same, providing a video of a ‘woman’ holding a large number of ‘kittens’, a ‘dog’ wearing a pearl earring, and a frightening video of a ‘jellyfish.’ X is also worth mentioning, see this video of a ‘capybara’ eating watermelon or this bizarre video of ‘tortoises’ and ‘turtles’ being used to make toothpaste.
These are just a few examples of the videos that are easily accessible with a simple search or scroll. While some pages are incredibly transparent about their use of AI and describe their use as art, others are not.
How to detect and combat AI-generated content
Detecting AI can be difficult. Learn the telltale signs to guard against unknowingly liking, sharing, or interacting with it. The following are useful tips to help start building your toolkit:
Slow down. When you’re scrolling and come across a piece of footage that catches your eye, take the time to examine it further.
Be critical and scrutinize the details
Beware of pages uploading compilations of both AI and authentic imagery. Sprinkling authentic content in with AI-generated footage can make you second guess your perception of real vs fake. Be a skeptic and dissect each clip.
Look at the creator’s page, some are transparent, and label their creations as AI either directly on or under their post.
Others may mention the use of AI in their bio…but fail to label their posts as AI.
Ask questions:
How does the video make you feel?
Are you uneasy?
Is it meant to evoke a strong emotional reaction?
Is it overly cute or outrageous?
What is the setting? Is it normal for an animal to be there?
What is it doing? Is that normal behavior?
Would you see this behavior in the wild, at home, or at a zoo?
Look carefully at the features, does its snout move in a funny way? What about the eyes, ears, or limbs?
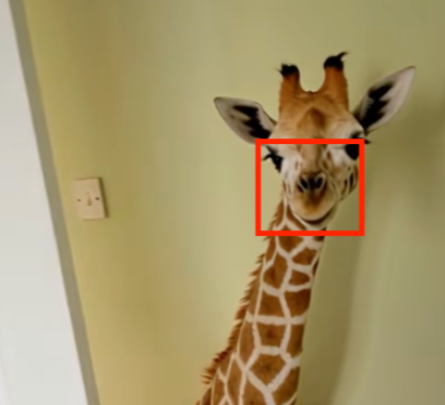
Use this video for example:
Ask yourself, why would a giraffe be inside a home?
Look at its snout, it's flat, appearing 2D, and when it moves it disappears for a moment.
AI GENERATED
This ‘jellyfish’ stumped some viewers. The creator’s bio makes no mention of AI. A viewer even left a comment seeming to affirm the ‘creature’ was a real species. To be clear, it is not.
What does it look like? Is it furry? What does the fur look like? Is it overly smooth or fluffy? Is there a high contrast between light and dark tones?
If it has a pattern, does that pattern change as it moves?
Does it have a cartoonish quality?
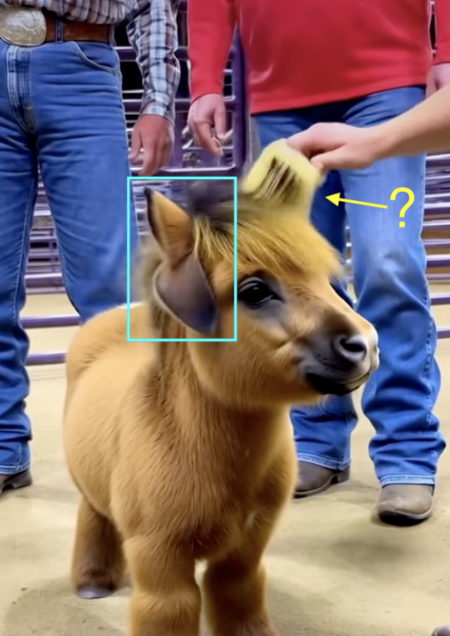
Take a look at this video of fake ‘micro highland cows.’ >>>>
Examine the high contrast in the fur, it appears almost like a painting or a cartoon.
Does it have features that belong to another species?
Are any of its limbs overly-human-like? Think long fingers, toes, human faces or features?
Examine the details: are they using tools or other items?
Does anything morph or meld?
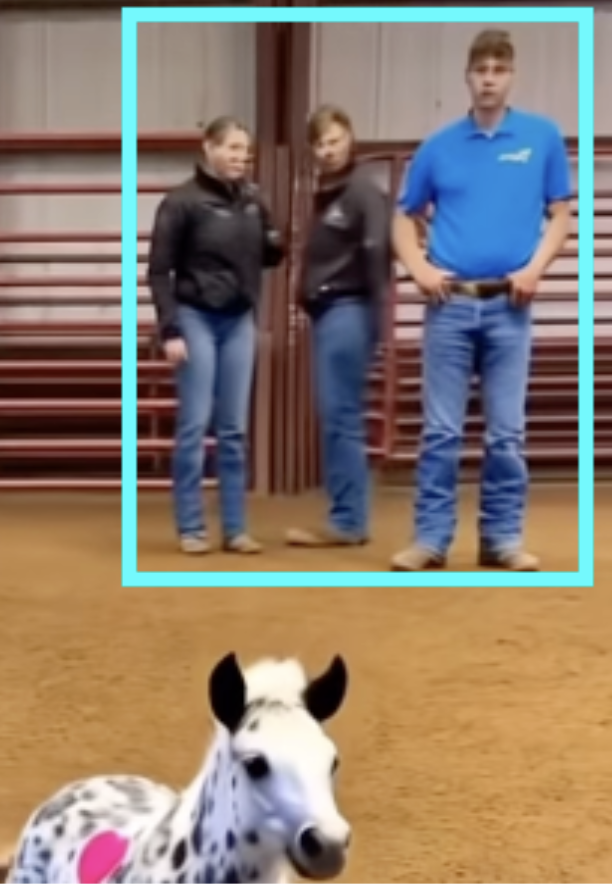
<<<<Examine this video of ‘people’ and mini ‘ponies:’
The first frame is some sort of pony-cow hybrid with two ears.
What is the tool they’re using to brush it?
It’s also painting-like with its fur defined and smooth.
Watch this video of a ‘dog’ with a pearl earring:
It has a human earlobe —that human earlobe transforms into a pearl.
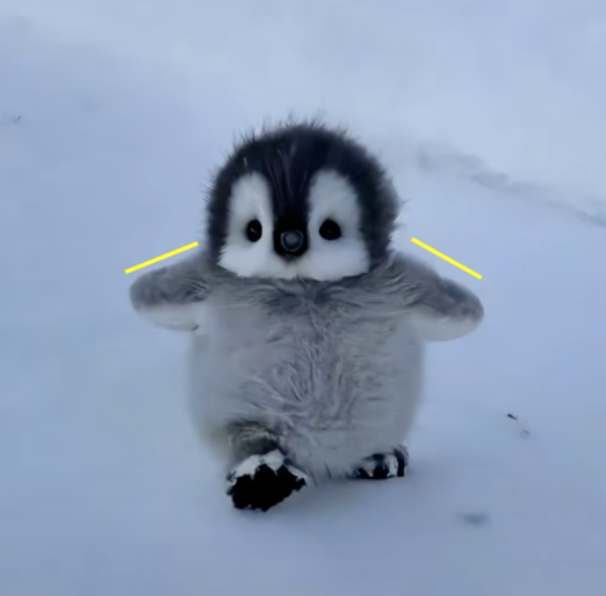
Take a look at this video. What stands out?
Watch its feet. They’re moving in an incredibly unnatural way, it appears to be skipping. It gains toe nails, then loses them, with its leg becoming a blob.
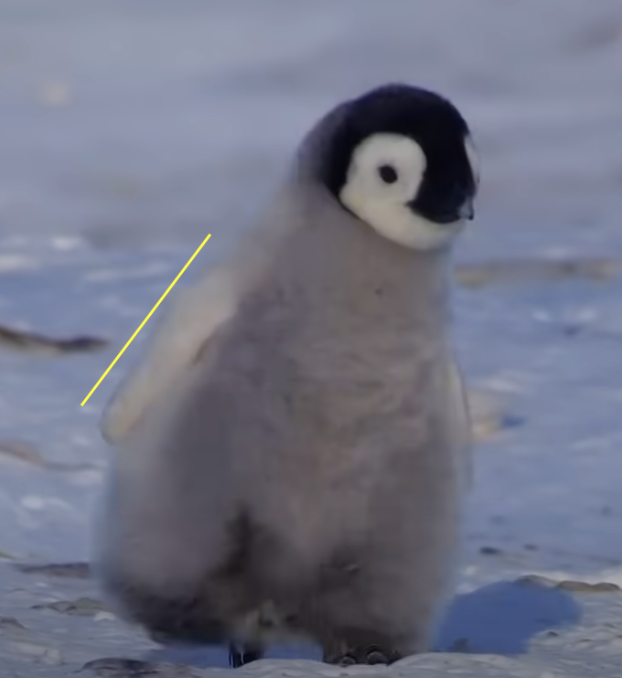
It’s meant to mimic the appearance of an emperor penguin chick, but it looks more like a stuffed animal than the real thing.
For comparison, check out this video from the BBC showing real chicks in their real environment. The faux-chick’s fuzz appears to be more like fur than feathers.
AUTHENTIC
VS
This video provides an example of gibberish signage:
Are there numbers or words? Can you make them out? Or is it just gibberish?
If the video has a human element, be sure to scrutinize them.
What do the hands look like? Do they have extra fingers?
Are the features definable or do they blending together?
How do they move?
When in doubt, slow down, be critical, and refrain from sharing or spreading deceptive, misleading, or entirely bogus content.
The Takeaway
Media literacy is a skill both publishers and audiences must develop and maintain. These examples may seem of little consequence, but as they flood social media the line between real and fake becomes blurred. A desensitized audience may believe and share manipulated content more readily. Providing tips to discern fact from fiction is the best way to combat more harmful uses of the ever-evolving technology.
AI Animal Slop is Infiltrating Social Feeds: A Guide For Detecting AI-Generated Content
AI-generated animals have flooded social feeds. Users across platforms are just a scroll or search away from being served phony footage of tiny penguins, mini horses, and more. While this content may seem benign, knowing how to detect AI in any scenario can fortify social media users and newsrooms against sharing misinformation.